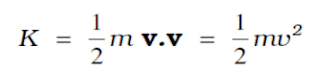WORK ENERGY AND POWER:
Work is the process of transferring energy from one object or form to another by means of a force.
When object A transfers energy to object B, the energy of object A decreases by the same amount as the energy of object B increases, we say that object A does work on object B.
The work done by the force is defined to be the product of component of the force in the direction of the displacement and the magnitude of this displacement.
It is a scalar quantity
2. Work done by a Variable Force:
In case of variable force work done is equal to,
3. Kinetic Energy:
The kinetic energy(K) of an object is a measure of the work an object can do by the virtue of its motion.
4.Potential Energy:
Potential energy is the ‘stored energy’ by virtue of the position or configuration of a body.
The Work Done by the external forces against conservative force on the body gets stored as its Potential Energy.
Gravitational Potential Energy,
V(h) = mgh
Elastic potential Energy,
5. Conservative and Non-Conservative Forces:
Conservative Forces
If the work done by a force depends only on initial and final positions, the force is called a conservative force. Work done is independent of the path taken by the particle.
For eg. Gravitational Forces, Spring Forces etc.
Non-Conservative Forces
A non-conservative force is a force for which the work done depends on the path taken. Work done is dependent on the path taken by the particle.
For eg. Frictional forces.
6. Energy Conservation:
Principle of Energy Conservation: The total mechanical energy of a system is conserved if the forces, doing work on it, are conservative.
This can be generalized too,
i.e; Total energy of the universe is constant. Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed.
7. Work Energy Theorem:
It states that, The work done by the sum of all forces acting on a particle equals the change in the kinetic energy of the particle
8. Power:
Power is defined as the time rate at which work is done or energy is
transferred.
Instantaneous Power,
9. Vertical Circular Motion:
Motion of particle in vertical circle is an example of a Non-uniform circular motion.
Tension at point A, (θ = 0)
Tension at point B, (θ = 90)
Tension at point C, (θ = 180)
Velocity at any point,
where is angle with the vertical line passing from center to A
Minimum velocity at A and C for completing the circle,
Collision:
Collision is short-duration interaction between two bodies or more than two bodies.
In collision there may be or may not be a physical interaction between colliding particles.
Elastic Collison:
If in a collision, kinetic energy after the collision is equal to the kinetic energy before the collision, the collision is said to be elastic.
Examples:
(1) Collision between atomic particles
(2) Bouncing of ball with same velocity after the collision with earth.
Inelastic Collision:
If in a collision kinetic energy after collision is not equal to kinetic energy before collision, the collision is said to inelastic.
Examples:
(1) Collision between two billiard balls.
(2) Collision between two automobile on a road.
Coefficient of restitution:
The ratio of relative velocity of separation and relative velocity of approach is defined as coefficient of restitution.
What is kinetic energy ?
What is Potential energy?
define kinetic energy ?
define Potential energy ?
what is the unit of kinetic energy ?
what is the unit of Potential energy ?
how to calculate kinetic energy ?
how to calculate Potential energy?
what is the unit of kinetic energy?
what is the unit of Potential energy ?